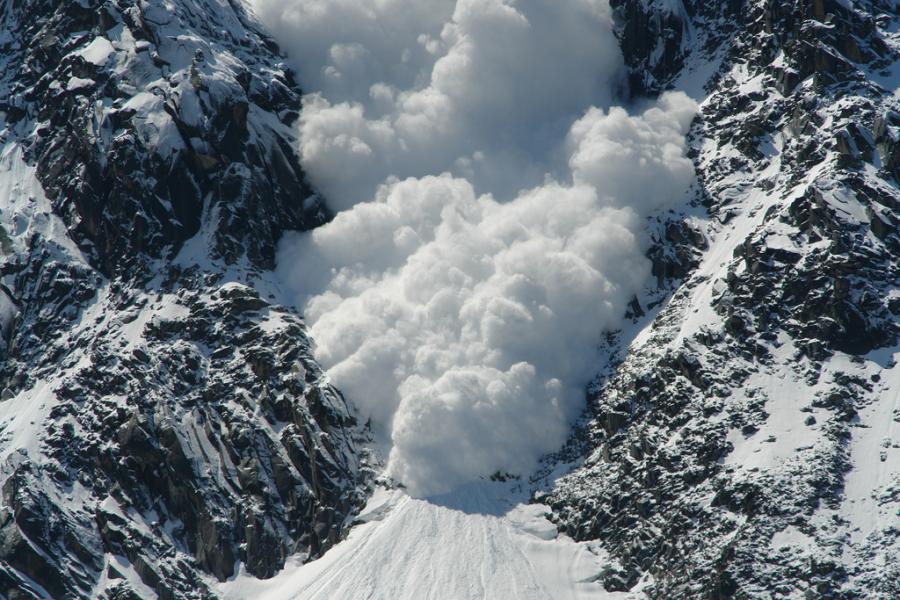
On Saturday a British expat living in Switzerland was killed by an avalanche on Mont Vélan south of Verbier near the Italian border. He was skiing the 3600m couloir d’Annibal with his brother, who survived. Both were apparently experienced freeriders with all the right equipment and the avalanche risk was 2/5. However the couloir is steep, upto 45°, and long.
On Saturday a British expat living in Switzerland was killed by an avalanche on Mont Vélan south of Verbier near the Italian border. He was skiing the 3600m couloir d’Annibal with his brother, who survived. Both were apparently experienced freeriders with all the right equipment and the avalanche risk was 2/5. However the couloir is steep, upto 45°, and long.
A 60-year-old German was also killed in an avalanche on Saturday on the Pigne d’Arolla, again in the far south of Valais.
Across the Alps a number of skiing and snowboarding fatalities occurred this weekend, bringing the total in the Alps to over 100 for the season. A large dump of fresh snow, high winds and the height of the freeriding season have all contributed.
However the fatalities need to be put in perspective. The number who die off-piste makes headlines, as do stories of drunk Brits topping themselves in the Alps, but skiing is relatively safe. The stats for Europe are patchy, but it would seem like there is roughly one fatality per million skier/snowboarders days, and roughly one serious injury per million skier/snowboarders days, based on stats collected by the NSAA in the USA. The USA boasts about 10 million skiers and snowboarders, who put in an average of about 5 days on the slopes per year. So in the USA maybe something around 50 people a year die on the slopes.
However, according to the National Safety Council, in a typical year 36,000 Americans died in motor-vehicle accidents; 5,000 pedestrians were killed; 9,000 died from unintentional public falls; 4,500 died from unintentional public poisoning; 2,500 people drowned while swimming in public areas and 1000 died while bicycle riding;
Incidentally, on the question of how many people ski rather than snowboard, The National Sporting Goods Association (NSGA) of the USA reports in 2011 there were 6.9 million skier and 5.1 million snowboarders. According to NSGA, 22.2 percent of snowboarders also ski, and conversely, 16.6 percent of skiers also snowboard.
Just thought you would be interested.